
Vertical Electrical Sounding (VES): A Simple Guide
Vertical Electrical Sounding (VES) is a
Since different types of soil, rock, and water-bearing layers conduct electricity differently, VES helps create a profile of the subsurface by showing how electrical resistivity changes with depth. High resistivity might indicate dry or rocky ground, while low resistivity often points to the presence of water or clay.
By analyzing these resistivity patterns, scientists, engineers, and hydrologists can map underground layers, locate aquifers, and even assess the quality of groundwater. VES is particularly valuable because it provides critical information without the need for expensive and invasive drilling, making it a cost-effective and environmentally friendly way to investigate what's happening below the surface.
In short, Vertical Electrical Sounding offers a window into the hidden structures beneath our feet, helping experts make informed decisions about water resource management, construction planning, and environmental conservation

How VES Works:
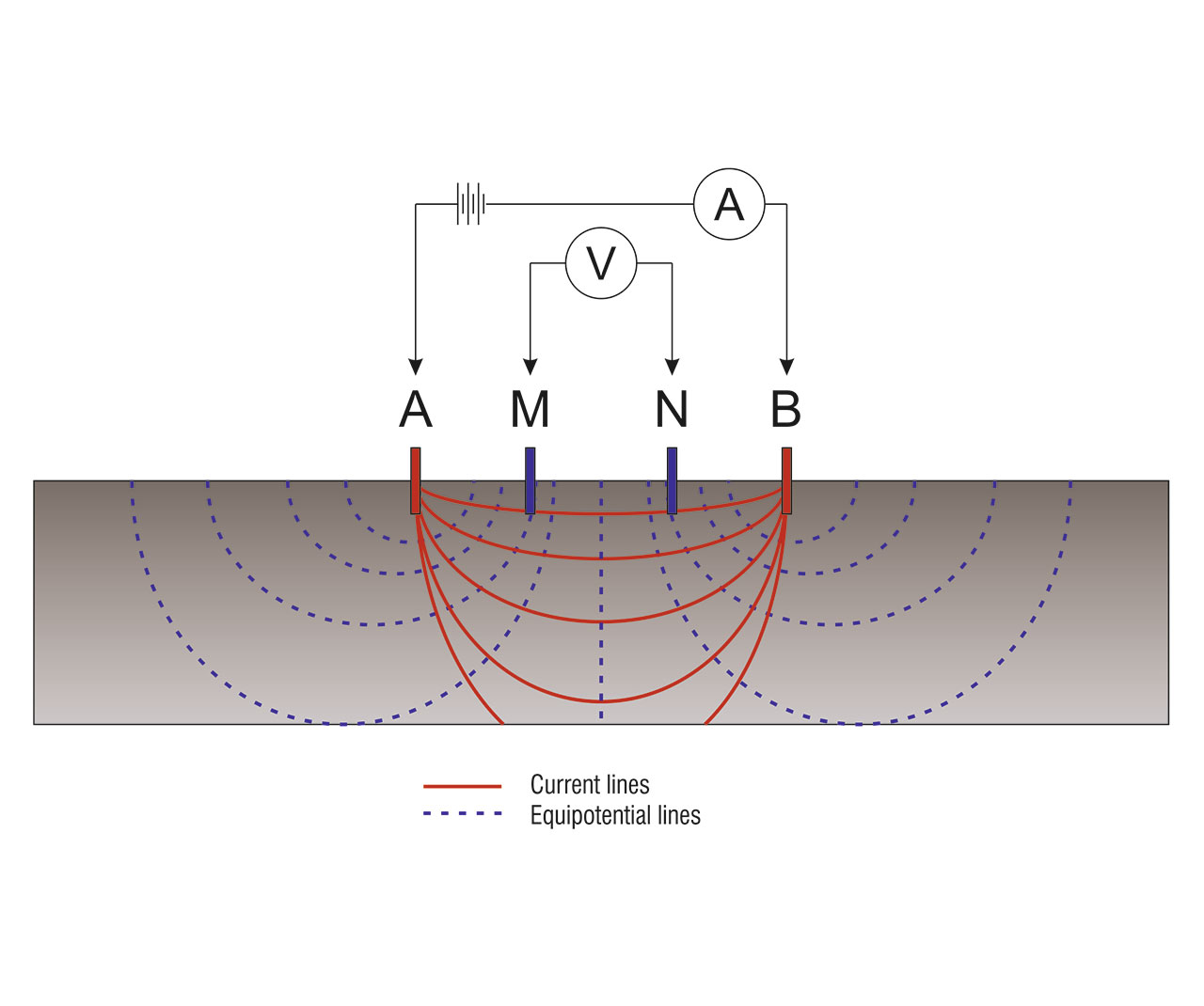
1. Electrode Configuration:
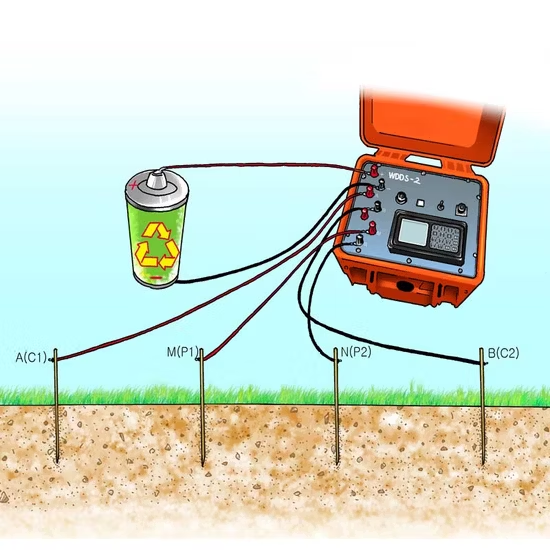
- Four electrodes are aligned linearly on the ground surface.
- The outer electrodes (A and B) serve as current electrodes, while the inner electrodes (M and N) function as potential electrodes.
2. Current Injection:
- A controlled electrical current is introduced into the ground through electrodes A and B.
- The resulting potential difference (voltage) is measured between electrodes M and N.
3. Electrode Spacing Adjustment:
- The spacing between the electrodes is systematically increased.
- This expansion allows the current to penetrate deeper into the subsurface layers.
4. Apparent Resistivity Measurement:
- At each electrode spacing, the apparent resistivity is calculated using the measured voltage and current values.
- The resistivity data is plotted against electrode spacing to generate a sounding curve.
5. Data Interpretation:
- The sounding curve is analyzed to infer the subsurface's layered structure.
- Variations in resistivity indicate different geological materials, aiding in identifying aquifers, bedrock, and other features.
Key Applications of VES:
Groundwater Exploration:
- Identifies the presence and depth of aquifers.
- Assesses the quality and quantity of groundwater resources.
Aquifer Characterization:
- Determines the thickness, depth, and extent of water-bearing formations.
- Evaluates the hydraulic properties of aquifers.
Geotechnical Investigations:
- Assesses soil and rock conditions for construction projects.
- Identifies zones of weakness or instability in the subsurface.
Environmental Studies:
- Detects contamination plumes and monitors remediation efforts.
- Maps saturated zones and old river channels (paleochannels).
Mining and Mineral Exploration:
- Maps subsurface structures and ore bodies.
- Assists in planning mine development and groundwater management.

Advantages of VES:
Cost-Effective:
- Requires minimal equipment and manpower.
- Offers a budget-friendly option for preliminary subsurface investigations.
Non-Invasive:
- Causes minimal disturbance to the environment.
- Suitable for sensitive or protected areas.
Depth-Resolved Data:
- Provides information on subsurface layers at various depths.
- Helps in constructing detailed geological models.
Versatility:
- Applicable in diverse fields such as hydrogeology, engineering, and environmental science.
Limitations of VES:
Limited Lateral Resolution:
- Primarily provides vertical profiles.
- May not detect lateral variations in subsurface properties.
Assumption of Horizontal Layers:
- Interpretation assumes that subsurface layers are horizontal and homogeneous.
- Complex geological settings can complicate data analysis.
Topographical Influences:
- Uneven terrain can affect measurement accuracy.
- Requires corrections or adjustments in hilly or rugged areas.

In summary, Vertical Electrical Sounding is a valuable geophysical tool for exploring and characterizing subsurface conditions. Its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and depth-resolved insights make it a preferred choice in various applications, especially in groundwater studies and environmental assessments.
From Homes to Industries — Tailored Water Audit Solutions That Save Costs & Resources.
© 2025 Kinetic Span Pvt Ltd. All Rights Reserved.

